Microsoft Dynamics 365 Cheat Sheet: Modules, Benefits & More

[ad_1]
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a comprehensive portfolio of software applications designed to benefit both small to midsize businesses and large enterprises that require more streamlined workflow capabilities and increased workplace efficiency. Once a business reaches a certain size, Dynamics 365 plays a critical role in providing automation tools that simplify operation management to meet the complexities that come with growth.
Dynamics 365 provides a cloud-based suite of enterprise resource planning and customer relationship management systems that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of many different organizations. Its integration capabilities, customization options and scalability make it a valuable asset that gives businesses the ability to analyze and process operational data. This, in turn, creates actionable information that can be accessed whenever it is needed.
Business applications of Microsoft Dynamics 365
Dynamics 365 is widely recognized for supporting a variety of business operations and scenarios across many different industries. With robust project management features, it can facilitate efficient planning and execution while also fostering more effective team collaboration.
PREMIUM: Choosing the right CRM for your organization.
Businesses can leverage Dynamics 365 to enhance productivity, streamline workflows and gain valuable insights from data analytics. Dynamics 365 facilitates seamless integration with other Microsoft products and third-party applications, ensuring adaptability and scalability to meet evolving business needs.
Financial management
Dynamics 365 offers intuitive financial management capabilities, including accounts payable and receivable, general ledger, budgeting and financial reporting (Figure A). It gives organizations the ability to manage their finances more efficiently and comply with existing regulatory requirements.
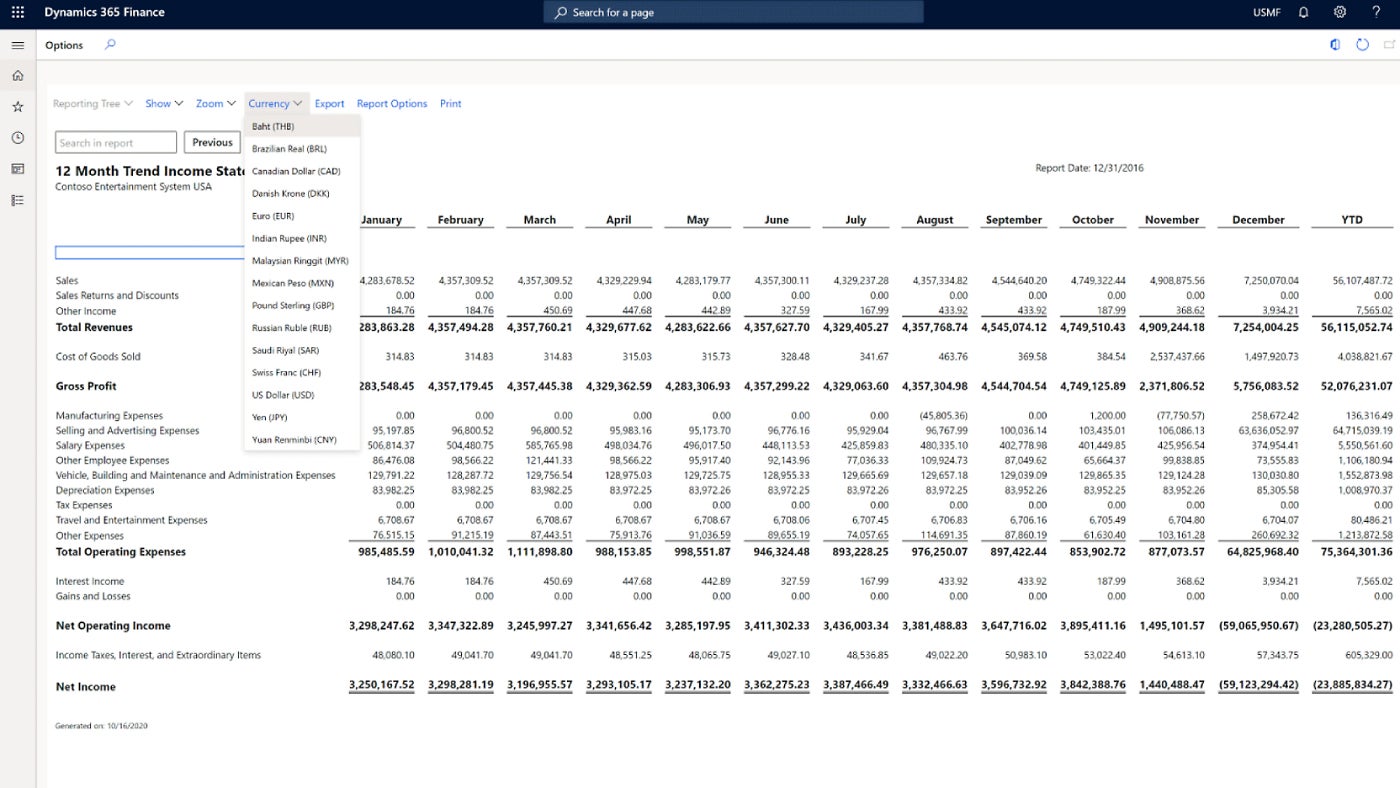
Supply chain management
A common use case for Dynamics 365 involves enabling businesses to streamline their supply chain processes by providing tools for inventory management, procurement, order fulfillment and demand forecasting (Figure B). This optimizes the flow of goods and services throughout the entirety of a business’s supply chain.
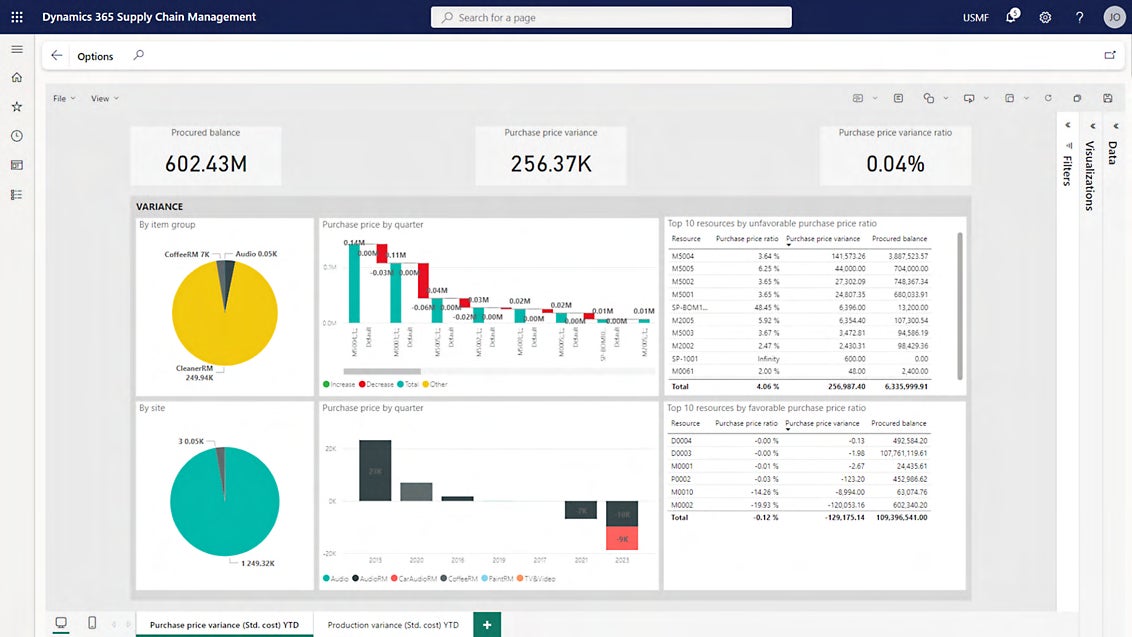
Customer relationship management
Dynamics 365 incorporates a CRM system that allows organizations to better manage their interactions with customers and prospects more effectively over time. It also provides features for sales automation, marketing automation and customer service to enhance customer engagement and satisfaction (Figure C).
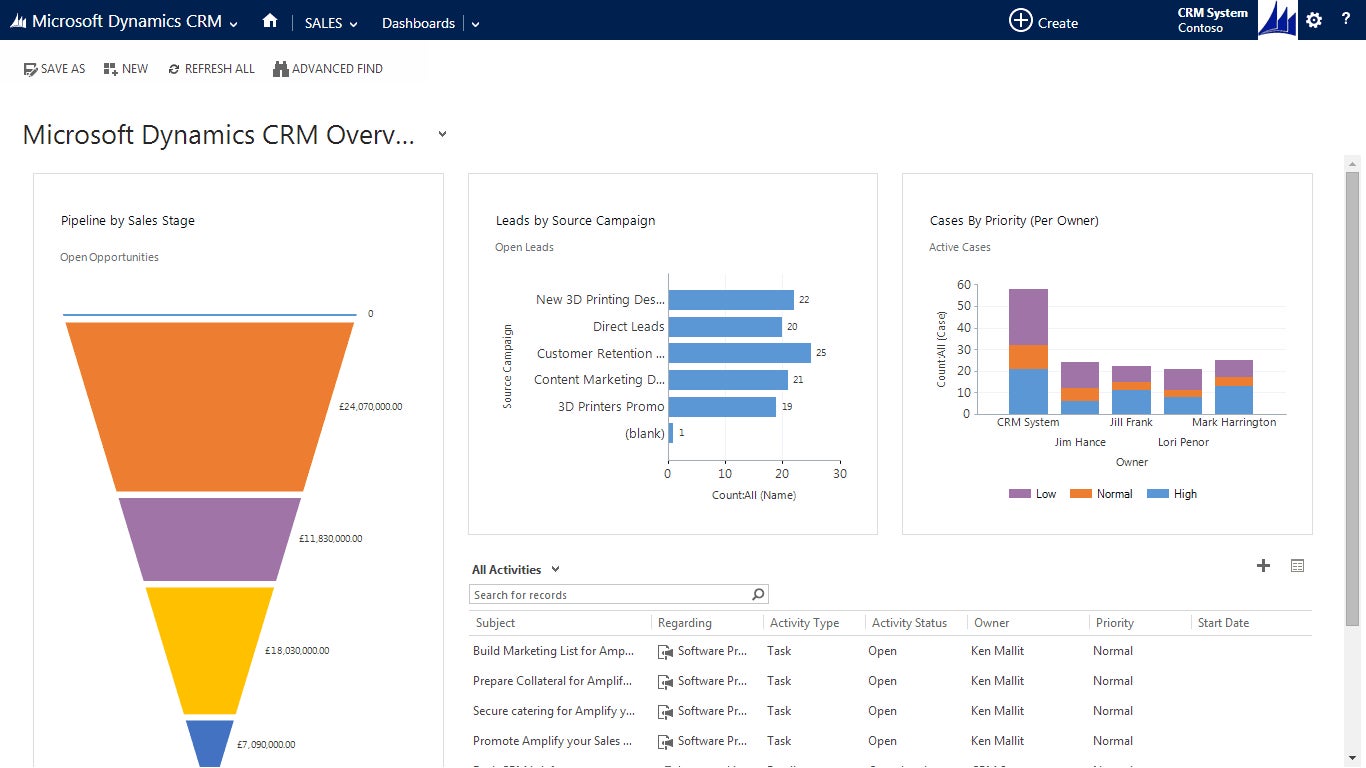
Sales optimization
The option for sales optimization is incredibly useful for automating sales processes, tracking leads and analyzing sales performance (Figure D). This empowers sales teams and creates a path for them to increase their productivity, improve collaboration and close deals much faster.
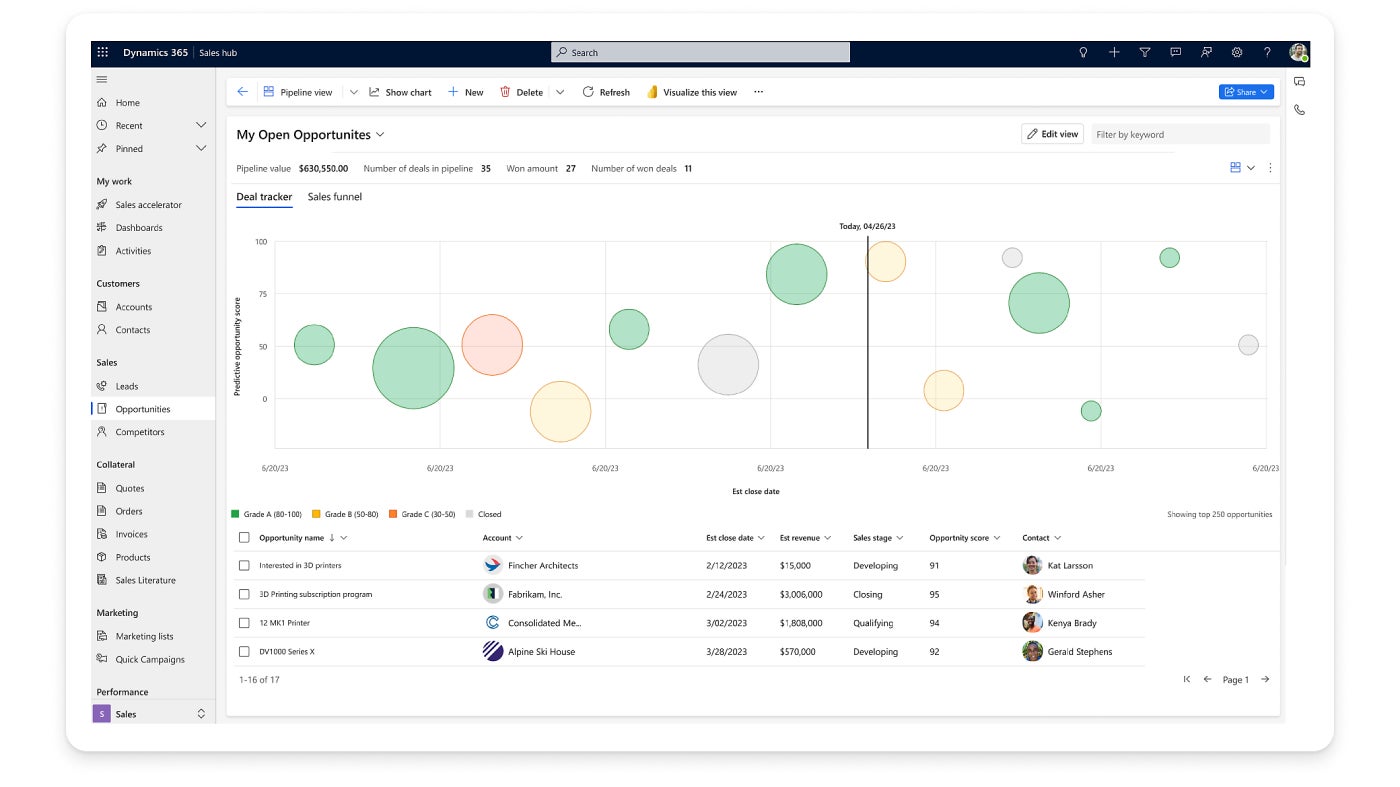
How to use Microsoft Dynamics 365
Using Dynamics 365 involves a systematic approach tailored to the specific needs and objectives of an organization. Businesses should begin by selecting the appropriate Dynamics solution that aligns with their specific requirements. This choice may depend on factors such as industry, size and functional needs. Suitable options can include Dynamics 365 Finance, Supply Chain Management, Sales, and Customer Service solutions.
Once a solution is selected, the organization can proceed with deployment planning. This involves determining whether to deploy Dynamics 365 on-premises, in the cloud or through a hybrid model. The deployment model is chosen based on factors such as existing IT infrastructure, scalability requirements and data security considerations.
Installation and configuration follow deployment planning. Organizations install the Dynamics solution and configure it to suit their specific business processes and workflows (Figure E). This includes setting up user accounts, defining security roles, customizing fields and forms and integrating with other systems as needed.
User training and adoption are essential to maximize the benefits of Dynamics 365. Organizations can provide comprehensive training programs to familiarize users with the platform’s features, functionality and best practices. Training may include hands-on workshops, online tutorials, user guides and ongoing support resources.
Once Microsoft Dynamics is in operation, organizations may use the platform for various day-to-day activities. This includes managing financial transactions, processing sales orders, tracking inventory levels and generating reports for analysis and decision-making.
Dynamics 365 makes use of a holistic approach that encompasses planning, deployment, training, operation and continuous improvement. By following these steps, organizations can harness the full potential of Dynamics 365 to drive business growth and innovation.
What software applications are available in Microsoft Dynamics 365?
Dynamics 365 offers a comprehensive suite of software applications designed to meet the diverse needs of modern businesses. These applications are tailored to streamline work processes, enhance productivity and drive growth. What follows is a general overview of the key applications available within the Dynamics 365 ecosystem.
- Sales: Manage customer relationships, track sales opportunities and automate sales processes to drive revenue growth.
- Customer service: Deliver exceptional customer support through case management and by referencing available knowledge bases.
- Field service: Optimize field operations with tools for scheduling, dispatching and tracking field service technicians.
- Marketing: Create and execute marketing campaigns, manage leads and analyze marketing performance to attract and retain customers.
- Finance and operations: Streamline financial management, supply chain management, manufacturing and retail operations for improved efficiency and profitability.
- Project service automation: Plan, track and deliver projects efficiently, including resource management and project accounting.
- Customer insights: Gain valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences using AI-driven analytics to inform strategic decision-making.
- AI applications: Leverage AI-driven applications for sales forecasting, customer service insights and virtual agents to enhance business performance.
These applications work seamlessly together within the Dynamics 365 platform, enabling organizations to unify their operations, gain actionable insights and deliver exceptional experiences to their customers.
What are Microsoft Dynamics 365’s competitors?
Dynamics 365 competes in the ERP and CRM software markets. Here are some of its key competitors and how they differ from Dynamics 365.
- Salesforce: Salesforce focuses primarily on CRM functionalities, whereas Dynamics 365 offers both CRM and ERP capabilities.
- Oracle ERP: While both Oracle and Dynamics 365 offer cloud-based ERP functionalities, they differ in terms of their depth of industry-specific solutions and their target markets.
- Workday Financial Management: Workday and Dynamics 365 cater to different aspects of business operations, with Workday focusing more on HR and finance management.
- HubSpot CRM: Unlike Dynamics 365, HubSpot’s offerings are primarily focused on marketing, sales and customer service and may lack comprehensive ERP functionalities.
- Daylite: Dynamics 365 provides extensive customization options and integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products, while Daylite offers customization options that may not be as extensive as Dynamics 365.
These are just a few examples of competitors to Dynamics 365 in the ERP and CRM software markets. Each competitor has its own strengths, target markets and areas of specialization, providing businesses with a variety of options to choose from based on their specific needs and requirements.
How can Microsoft Dynamics 365 fit into a user’s tech stack?
Dynamics 365 can serve as a central component of a user’s tech stack, playing a vital role in managing various aspects of business operations. The platform can be used as a central hub within a tech stack and can facilitate data management, productivity, automation and integration with other tools and services. Its flexibility and scalability make it an essential component for businesses seeking to streamline operations, drive innovation and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
[ad_2]
Source Credit




